When you deploy a package that contains a PowerShell step, PDQ Deploy bundles the contents of your PowerShell step and adds some basic error handling before sending it to a target. This bundle contains two files: user1.ps1 and Error Handling Wrapper.ps1. These files are created automatically when deploying a package that contains PowerShell and allows PDQ Deploy to better report on errors that occur during PowerShell deployments.
The user.ps1 script contains the PowerShell code that is contained in a PowerShell step. The Error Handling Wrapper.ps1 script contains a call to run user.ps1 as well as basic error handling. This allows PDQ Deploy to properly display any errors that happen during a PowerShell deployment.
Without basic error handling, PowerShell will return a value of 0 to PDQ Deploy when a PowerShell step is run on a target. This is because PowerShell only determines whether or not the script was able to run rather than what errors or exceptions happen during a deployment.
If you explicitly add an exit code to your PowerShell step or if you call a PowerShell script that contains an exit code, it will be returned as $lastexitcode after user.ps1 is called.
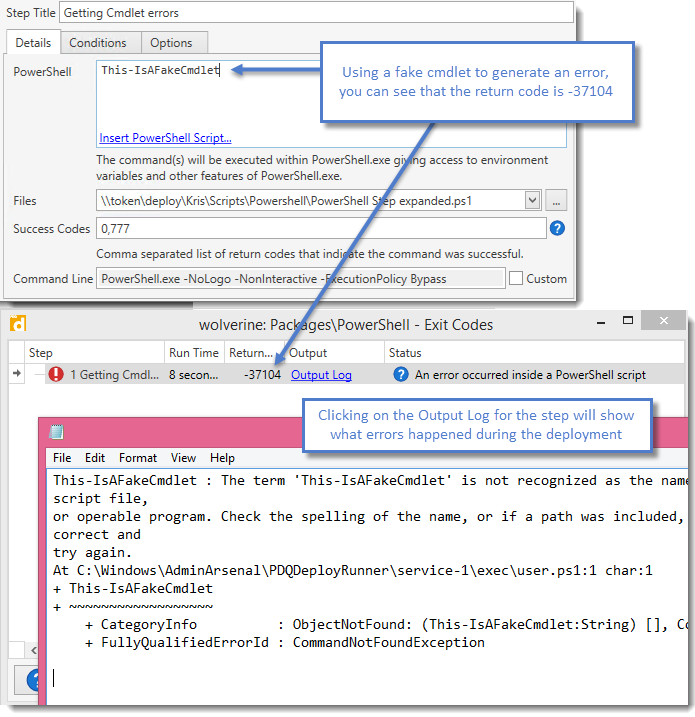
Native PowerShell cmdlets do not normally generate exit codes. Instead, any errors or exceptions are recorded in PowerShell's global variable $error (see automatic variables on Technet for more information). When deploying a PowerShell step, PDQ Deploy looks at the contents of $error for any entry that has a property and value of writeErrorSteam = $true. If any entries are found, targets with PowerShell version 3 or higher will return with exit code -37104. PowerShell version 2 targets will return with exit code 37105.
IMPORTANT: PowerShell version 1 is not supported in PDQ Deploy.
Without basic error handling, PowerShell will return a value of 0 to PDQ Deploy when a PowerShell step is run on a target. This is because PowerShell is simply returning whether or not the script was able to run rather than what errors or exceptions happen during a deployment.
The following are examples of Error Handling:
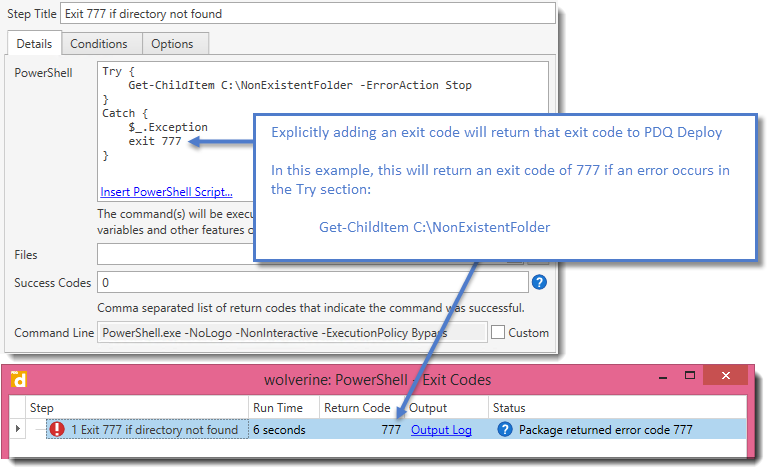
1.Explicitly adding an exit code:
In a PowerShell step, we used the following code.
Try {
Get-ChildItem C:\NonExistentFolder -ErrorAction Stop
}
Catch {
$_.Exception
exit 777
}
This will return a value of 777 if there is an error or exception that occurs.
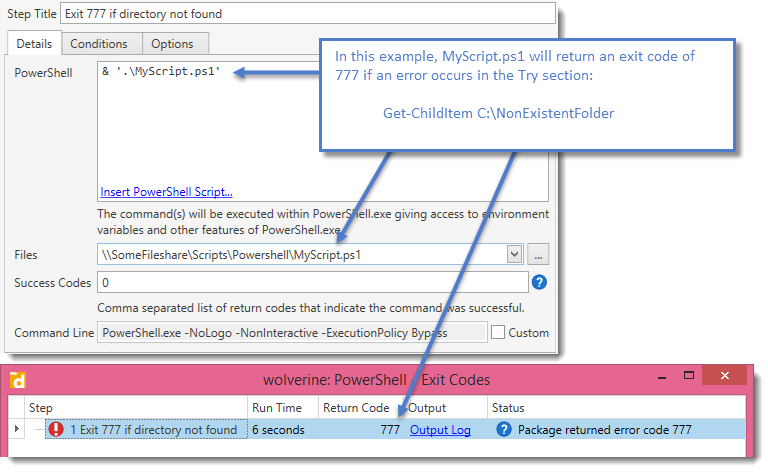
2.Adding exit codes to a script and then calling the script:
In a PowerShell script, we used the same example code listed in example 1, but saved it as MyScript.ps1:
Try {
Get-ChildItem C:\NonExistentFolder -ErrorAction Stop
}
Catch {
$_.Exception
exit 777
}
This will return a value of 777 if there is an error or exception that occurs when the script is called and the step is deployed to a target:
3.Native PowerShell cmdlet errors:
You will need to handle any exceptions within your PowerShell code to account for these errors.
© 2020 PDQ.com Corporation. All rights reserved.
PDQ.com is a trademark of PDQ.com Corporation. All other product and company names are the property of their respective owners.
Help Version: 19.1.15.0