A PDQ Inventory tool contains the command to be run using the cmd.exe or PowerShell. Tools can be Remote, Local, or System. This section describes how to create and configure tools. (Enterprise mode is required to create and edit tools). Your own Tools cannot be called against more than one computer at a time.
An alternative to creating a new tool from scratch is to base a new tool on a tool downloaded from the Tools Library. Simply duplicate and rename the tool that is similar to the tool you need, then edit it to meet your requirements. Examining tools is also a great way to learn how tools are configured. For information about duplicating and editing tools, see Duplicating Tools.
NOTE: You can create a PDQ Deploy package with the command(s) used in this window by clicking Tools > Create PDQ Deploy Package. This launches PDQ Deploy and opens a new package window with the command entered. Configure the remainder of the package to your needs and click Save. (Enterprise mode and PDQ Deploy required to create a package.)
This section contains the following:
For more information on creating your own Tools, see the following:
VIDEO: Using Remote Commands in PDQ Inventory
Using Remote Commands in PDQ Inventory
(https://youtu.be/tUPVa5ArP_Y)
WEBCAST: PDQ Live! : Custom Tools & The Tools Library in PDQ Inventory
Custom Tools & The Tools Library
(https://youtu.be/2Tnu6Vcq-rg)
The Tool Window (Edit Mode)
Tools are created within Edit Mode of the Run Command window. To access on the Main Console window click on Tools in the tree. On the Tools page, select the Tools Menu tab and click New > Tool.
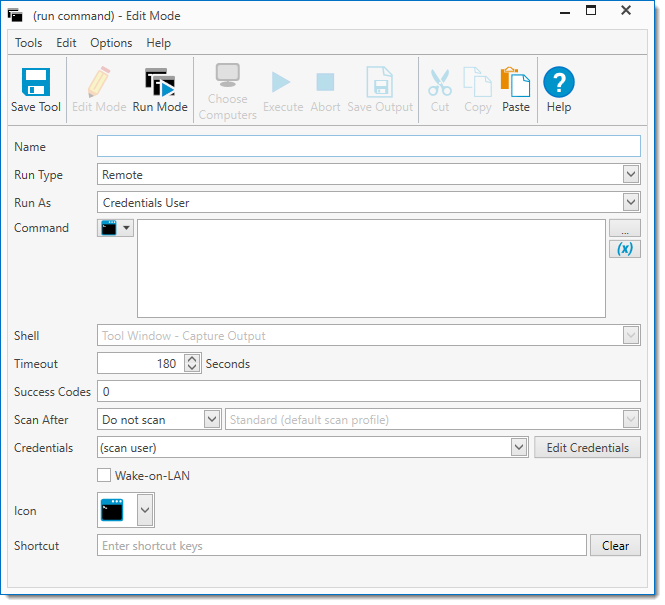
The following table reviews each option in the Edit Mode of the Run Command window.
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
Name |
The name of the tool. You are likely to create many tools so it's important to name them clearly and consistently. We suggest using names that include a hint about what is contained in the command. |
|
Run Type |
The type of tool either Remote, Local (default), or System. NOTE: Options available in this window are dynamically available depending on the type of tool chosen. |
|
|
Remote |
The commands run remotely on selected targets. |
Local |
The command runs on the local computer, not on the target. This is an important distinction, since a command run through the Tools menu would need to use variables and/or UNC pathnames to be able to perform the command against a target. For example, remotely opening the ADMIN$ share on a target is executed locally with a command, explorer.exe "\\$(Computer:TARGETHOSTNAME)\ADMIN$". This is the default tool type. |
|
The tool will run from anywhere within the program without needing a computer to be selected. This is not typically checked if the program will be run on the local PDQ Inventory console (for example, opening up Active Directory Users and Computers). If left unchecked, a computer must be selected for the tool to be available. IMPORTANT: System Tools cannot be used in conjunction with computer specific variables. For information see Computer Variables. |
||
Run As |
|
|
|
Credentials User |
Silently executes the tool on the target computers using the credentials specified in the tool. This is the default selection. This setting is appropriate for the vast majority of tools. |
Credentials User (Interactive) |
This setting is the same as Credentials User with one important exception—the Windows process running the tool is run in interactive mode. This setting is most appropriately used for individual tools that require user input, but the overall process still requires Administrator rights that logged on users may not have. This type of tool requires more processing resources. |
|
Local System |
Executes tools using the local System account on the target computer. PDQ Inventory connects to the target computer then runs the tool using Local System credentials. |
|
Logged on User |
Attempts to run tools in Interactive mode as the Logged On User of the target machine. This setting is used for tools that are per user or when the logged on user needs to provide information for the tool to succeed such as a license key. It can also be used to modify the HKEY-CURRENT-USER registry hive for the logged on user or to access user-specific settings such as %APPDATA% or the logged on user’s User directory. |
|
Command |
The command of the tool. This is the command that will be run as though run from the Windows command or PowerShell. This can be a command line instruction, a path to an executable, or a script. Choose between Command (cmd) You can write the path or use the file picker Insert a variable by selecting the variables button NOTE: Using the file picker will display the file name to be run. The script itself will not be displayed in the window. |
|
Shell |
The behavior of the output in Run Mode, Command window, or PowerShell window after launching the tool. |
|
|
Tool Window - Capture Output |
Upon launching the tool, the Run Command window is opened which captures the output. The output can then be saved to a .txt file. |
No Shell - Ignore Output |
The tool runs without a shell opening and output is not captured. NOTE: The ability to use the Run Mode is disabled with this choice. The tool must be run in the main console window after it is created. |
|
Close Shell on Completion |
The shell (either Command or PowerShell) used to run the command is displayed while the command runs, but closes immediately upon completion. NOTE: The ability to use the Run Mode is disabled with this choice. The tool must be run in the main console window after it is created. |
|
Leave Shell Open |
The shell (either Command or PowerShell) used to run the command remains open upon completion of the command. NOTE: The ability to use the Run Mode is disabled with this choice. The tool must be run in the main console window after it is created. |
|
Timeout |
The length of time to run the command before it is automatically aborted (default is 180 seconds). NOTE: Timeout is only available for a Remote Tool. |
|
Success Codes |
By default, 0 is selected, which means the command was successful. You can provide additional success codes in a comma-separated list. NOTE: Success Codes are only available for a Remote Tool. |
|
Scan After |
Initiates an inventory scan after the command is run to identify the full inventory on each workstation. A scan is attempted on target computers even if the command fails. You may choose whichever Scan Profile has been configured. The default Scan Profile is defined in the Scan Profiles page. The most commonly used are Standard or Applications. NOTE: The ability to Scan After is only available for a Remote Tool. |
|
Credentials |
The credentials that will be used for the listed computer(s). The user must be a local administrator on the target computer(s). |
|
|
Edit Credentials |
Click to edit the existing credentials or add a new set of administrator credentials. |
Wake-on-LAN |
Initiates a distributed Wake-on-LAN (WOL) event on all listed computers prior to running the remote command. NOTE: Wake-on-LAN is only available for a Remote Tool. |
|
Icon |
The icon used to identify the tool. If no icon is selected, it will default to either the Command or PowerShell icon as chosen for the shell type. |
|
Shortcut |
The keyboard shortcut used to launch the tool. Simply enter the key combination on your keyboard to assign a new shortcut. The shortcut takes the form of Modifier+Key and is created by selecting this field and then pressing the keys in the correct order. The valid modifiers are Shift, Ctrl, and Alt. Shift cannot be used by itself. Examples include: •Ctrl+Alt+Q •Ctrl+Shift+8 •Shift+Alt+B •Alt+F1 IMPORTANT: This shortcut should not conflict with any other in the application or it will not work properly. |
|
Computer Specific Variables
You can use variables with tools. The Command Line field of the Custom Computer Tool window will accept environmental variables (for example, %PROGRAMFILES%, %WINDIR%, %SYSTEMDRIVE%, etc.), as well as variables defined within PDQ Inventory (variables are not case sensitive). The computer specific variables available within PDQ Inventory are as follows:
IMPORTANT: Computer specific variables starting with %TARGET are no longer supported and will need to be replaced with a computer variable starting with $(Computer:TARGET. Additionally, computer specific variables cannot be used when the System Tool is checked. For more information, see System Tool.
Computer Specific Variable |
Description |
|---|---|
$(Computer:TARGET) |
The name of the computer. |
$(Computer:TARGETHOSTNAME) |
The full domain name of the computer. |
$(Computer:TARGETIPADDRESS) |
The IP address of the computer. |
$(Computer:TARGETMACADDRESS) |
The MAC address of the computer. |
$(Computer:TARGETOSNAME) |
The name of the computer's operating system |
$(Computer:TARGETSERIALNUMBER) |
The serial number of the computer, if available. |
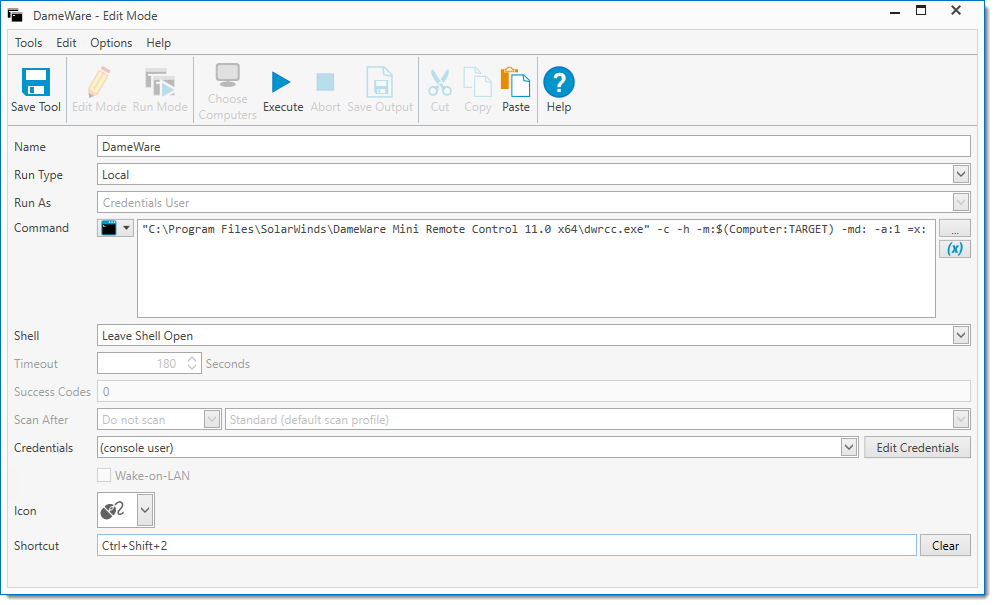
The example below shows a Tool which opens a DameWare 11 remote control session against a selected computer, using the Command "C:\Program Files\SolarWinds\DameWare Mini Remote Control 11.0 x64\dwrcc.exe" -c -h -m:$(Computer:TARGET) -md: -a:1 -x:
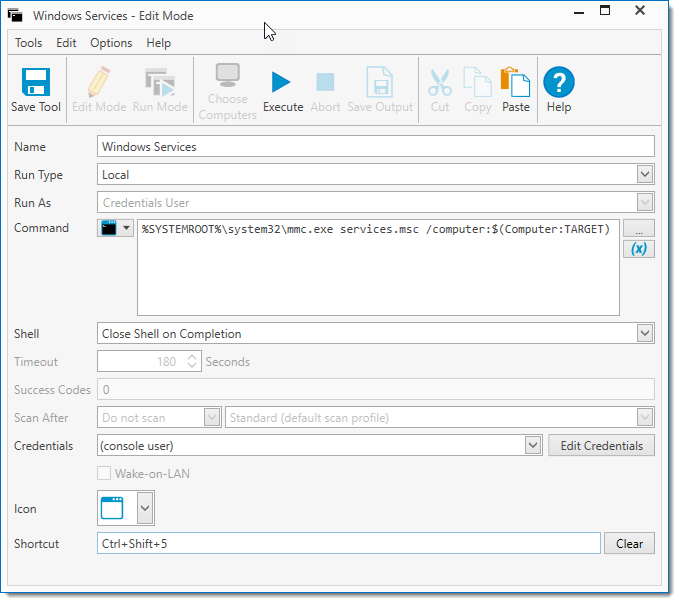
The example below shows a Tool which opens MMC and loads the Services.msc snap-in and connects to the selected computer, using the Command %SYSTEMROOT%\system32\mmc.exe services.msc /computer:$(Computer:TARGET)
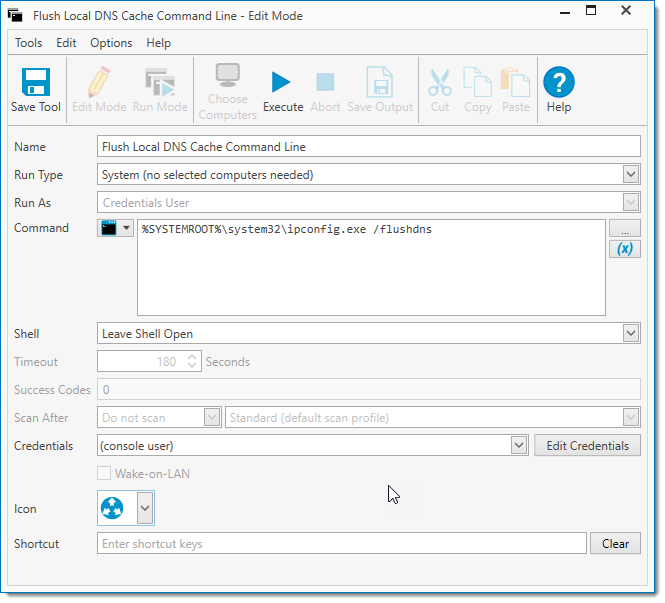
The example below shows a Tool which flushes your DNS cache in Windows, using the Command %SYSTEMROOT%\System32\ipconfig.exe /flushdns
© 2024 PDQ.com Corporation. All rights reserved.
PDQ.com is a trademark of PDQ.com Corporation. All other product and company names are the property of their respective owners.
Help Version: 19.3.590.0